Observations of stream habitat can tell us about its health. Throughout the sample reach, crews record the depth, assess how swiftly the stream is flowing, and count submerged branches and logs. At 11 equally spaced transects (cross-sections), crews also evaluate the size of rocks and pebbles in the stream, record the amount of overhanging vegetation, and identify signs of human activity.
How are these data used?
Observations are used to determine values for four physical habitat indicators.
Physical Indicators

Riparian vegetation cover measures the amount of overhanging tree limbs, shrubs and plants growing along the shore. Healthy, multilayered vegetation can provide a buffer from the effects of disturbance by slowing runoff and erosion, filtering nutrients and providing shade. Cover also provides food and habitat for fish and other organisms.
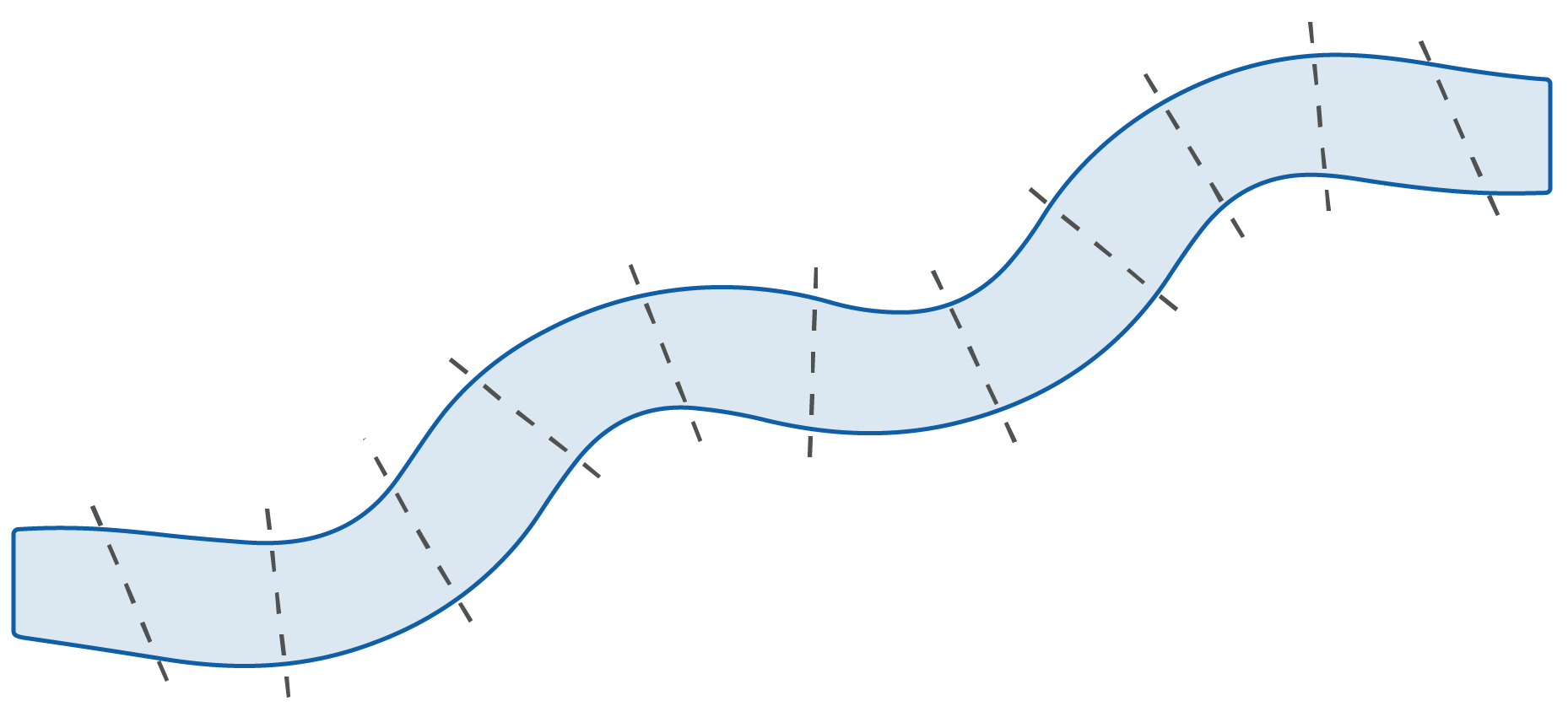
Where is riparian vegetation observed?
characteristics throughout
the sample reach.
To learn more, see the
NRSA Field Operations Manual.